


Wet Chemical For Kitchen Fire
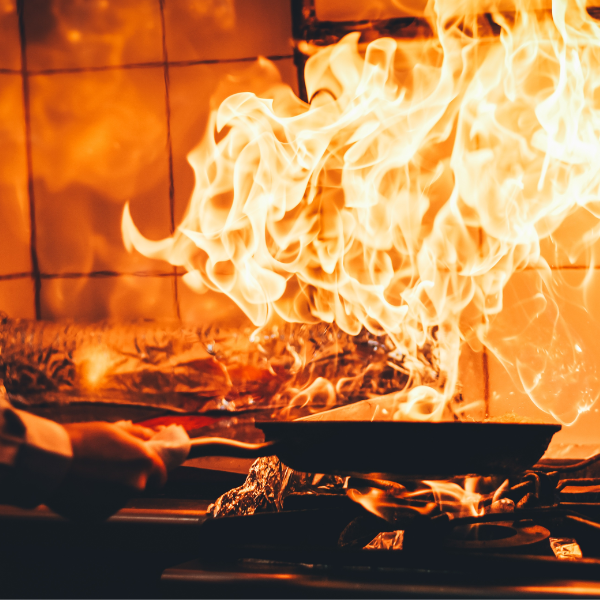
USAFE Wet Chemical Suppressants is designed for use only in Kitchen Fire Extinguisher, Cooking Oil Fire, or restaurant fire suppression systems or Fire Class K/F .This ‘‘liquid’’ agent will combat grease-related fires as found in restaurant appliances and ventilating equipment. It should not be used for fires involving energized electrical hazards.
USAFE Liquid Fire Suppressant is a specially-formulated, aqueous solution of organic salts. The agent is pre-mixed, eliminating the need for dilution before system charging. When used as an extinguishing agent, it will produce no toxic by-products. These extinguishing agent work by instigating a chemical reaction with fats and oils. This reaction reduces the temperature and eliminates the heat, causing flames extinguishment.
KEY FEATURES :
- Fast flame knock-down and secured of grease-related fires n Provides a cooling effect which further enhances its ability to prevent re-flash or re-fire.
- Designed for a wide variety of restaurant hazards
- Ease of recharge and post-fire cleanup
- Can be used in Automatic Kitchen Fire Suppression System
PERFORMANCE
When used in the Kitchen Fire Extinguisher or Kitchen Fire Suppression system, It is extremely effective on fires in restaurant ventilating equipment – hoods and ductwork, as well as in a variety of cooking appliances like deep-fat fryers, grid dles, range tops, and several types of broilers and charbroilers.
As the agent is sprayed in fine droplets (atomized) onto an appliance grease fire, it provides excellent flame knock-down, surface-cooling, and fire-securing capabilities. When the agent reacts with the hot grease, it forms a layer of foam on the surface of the fat. This soap-like blanket of foam acts as an insulator between the hot grease and the atmosphere, helping to prevent flammable vapours from escaping and reducing the chance for flame re-ignition.
HOW DO WET CHEMICAL EXTINGUISHERS WORK?
Wet Chemical Fire Extinguishers contains a solution of potassium which effectively attacks the flame in two methods:
Firstly the mist cools the fire and lowers the temperature to stop the fire spreading, also prevents
splashing of the hot oils/fat
Secondly the potassium salts react with the hot oil and causes the process of saponification, coating the surface of the cooking oil or fat in soapy foam that is non combustible and acts as a barrier between the fat and oil.

